libvpx中的decode_tiles
libvpx中的decode_tiles有三种:多线程单行解码的decode_tiles_row_wise_mt、多线程多行解码的decode_tiles_mt、单线程解码的decode_tiles。
# decode_tiles_mt
先来看多线程多行解码的decode_tiles_mt
static const uint8_t *decode_tiles_mt(VP9Decoder *pbi, const uint8_t *data,
const uint8_t *data_end) {
2
函数开始。
VP9_COMMON *const cm = &pbi->common;
const VPxWorkerInterface *const winterface = vpx_get_worker_interface();
2
首先是获取到VP9_COMMON和一个VPxWorkerInterface。这个VP9_COMMON已经见过很多了,这个VPxWorkerInterface长这样:
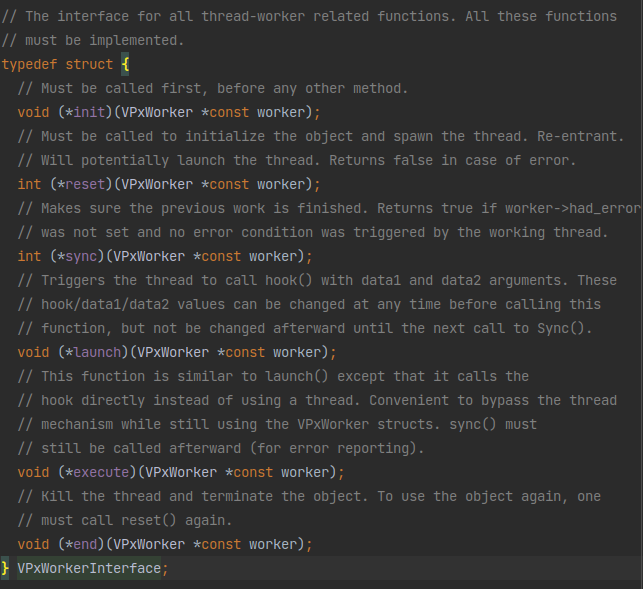
从注释看就是一个VPxWorker的执行器,用于在线程中执行VPxWorker中的操作。从注释上看主要操作是launch和execute里面在调用VPxWorker里面的hook函数。这个VPxWorker也很简单:

所以这个hook函数应该就是多线程中每个操作所执行的地方了。后面应该会有对这一项赋值并且调用VPxWorkerInterface的launch或者execute的地方。
const uint8_t *bit_reader_end = NULL;
后面要用的的不知道什么变量。
VP9LfSync *lf_row_sync = &pbi->lf_row_sync;
点进去看看,“lf”是环路滤波的英文缩写,这个变量是多线程环路滤波相关的变量。
YV12_BUFFER_CONFIG *const new_fb = get_frame_new_buffer(cm);
const int tile_cols = 1 << cm->log2_tile_cols;
const int tile_rows = 1 << cm->log2_tile_rows;
2
3
这几个操作在《libvpx解码过程解读》里面已经见过了,不必多讲。
const int num_workers = VPXMIN(pbi->max_threads, tile_cols);
这里设置了一下worker数量。这个VPXMIN点进去看其实是一个比大小的宏,所以这里是取最大线程数max_threads和分块行的数量tile_cols中的最小值作为线程数?这意思应该是多线程并行只是在同一行中的每一列之间并行,而行与行之间是串行的。
int n;
assert(tile_cols <= (1 << 6));
assert(tile_rows == 1);
(void)tile_rows;
2
3
4
5
一些判断。怎么有assert(tile_rows == 1)?这不是多行多线程吗
init_mt(pbi);
初始化多线程。
// Reset tile decoding hook
for (n = 0; n < num_workers; ++n) {
VPxWorker *const worker = &pbi->tile_workers[n];
TileWorkerData *const tile_data =
&pbi->tile_worker_data[n + pbi->total_tiles];
winterface->sync(worker);
if (pbi->lpf_mt_opt && cm->lf.filter_level && !cm->skip_loop_filter) {
tile_data->lf_sync = lf_row_sync;
tile_data->lf_data = &tile_data->lf_sync->lfdata[n];
vp9_loop_filter_data_reset(tile_data->lf_data, new_fb, cm, pbi->mb.plane);
tile_data->lf_data->y_only = 0;
}
tile_data->xd = pbi->mb;
tile_data->xd.counts =
cm->frame_parallel_decoding_mode ? NULL : &tile_data->counts;
worker->hook = tile_worker_hook;
worker->data1 = tile_data;
worker->data2 = pbi;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
终于看见前面说的给hook赋值的地方了!这里是一个循环给每个pbi->tile_workers中的每个worker和pbi->row_mt_worker_data->thread_data中的每个worker要用的数据赋值。所以很明显这个tile_worker_hook就是多线程解码tile1的核心函数。
// Load tile data into tile_buffers
get_tile_buffers(pbi, data, data_end, tile_cols, tile_rows,
&pbi->tile_buffers);
2
3
一个get_tile_buffers把data里的tile数据加载到pbi->tile_buffers里:
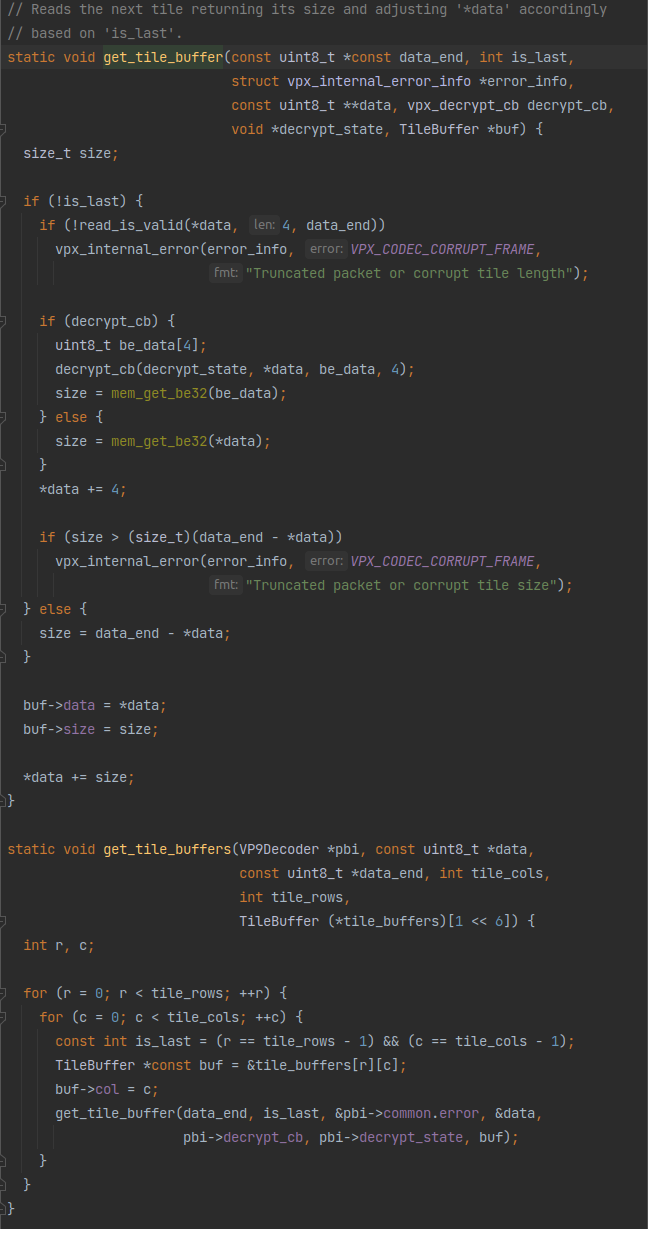
笑了😂,就是一行一行一列一列的拷贝。
// Sort the buffers based on size in descending order.
qsort(pbi->tile_buffers, tile_cols, sizeof(pbi->tile_buffers[0]),
compare_tile_buffers);
2
3
排了个序?可能是排序了多线程可以算的更快?
if (num_workers == tile_cols) {
// Rearrange the tile buffers such that the largest, and
// presumably the most difficult, tile will be decoded in the main thread.
// This should help minimize the number of instances where the main thread
// is waiting for a worker to complete.
const TileBuffer largest = pbi->tile_buffers[0];
memmove(pbi->tile_buffers, pbi->tile_buffers + 1,
(tile_cols - 1) * sizeof(pbi->tile_buffers[0]));
pbi->tile_buffers[tile_cols - 1] = largest;
} else {
int start = 0, end = tile_cols - 2;
TileBuffer tmp;
// Interleave the tiles to distribute the load between threads, assuming a
// larger tile implies it is more difficult to decode.
while (start < end) {
tmp = pbi->tile_buffers[start];
pbi->tile_buffers[start] = pbi->tile_buffers[end];
pbi->tile_buffers[end] = tmp;
start += 2;
end -= 2;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
这应该是把块的任务分给每个线程吧。上面的num_workers == tile_cols的情况可以一个线程一个任务,不这样就得有一个线程运行多个任务(前面的排序应该也是为了这个?大任务尽量和小任务一起交给一个线程,尽可能保证处理时间均衡,效率最高)。
// Initialize thread frame counts.
if (!cm->frame_parallel_decoding_mode) {
for (n = 0; n < num_workers; ++n) {
TileWorkerData *const tile_data =
(TileWorkerData *)pbi->tile_workers[n].data1;
vp9_zero(tile_data->counts);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
初始化线程帧计数?
{
const int base = tile_cols / num_workers;
const int remain = tile_cols % num_workers;
int buf_start = 0;
for (n = 0; n < num_workers; ++n) {
const int count = base + (remain + n) / num_workers;
VPxWorker *const worker = &pbi->tile_workers[n];
TileWorkerData *const tile_data = (TileWorkerData *)worker->data1;
tile_data->buf_start = buf_start;
tile_data->buf_end = buf_start + count - 1;
tile_data->data_end = data_end;
buf_start += count;
worker->had_error = 0;
if (n == num_workers - 1) {
assert(tile_data->buf_end == tile_cols - 1);
winterface->execute(worker);
} else {
winterface->launch(worker);
}
}
for (; n > 0; --n) {
VPxWorker *const worker = &pbi->tile_workers[n - 1];
TileWorkerData *const tile_data = (TileWorkerData *)worker->data1;
// TODO(jzern): The tile may have specific error data associated with
// its vpx_internal_error_info which could be propagated to the main info
// in cm. Additionally once the threads have been synced and an error is
// detected, there's no point in continuing to decode tiles.
pbi->mb.corrupted |= !winterface->sync(worker);
if (!bit_reader_end) bit_reader_end = tile_data->data_end;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
开始执行了!其实就是for循环用winterface->execute异步启动每一个worker,最后一个worker用winterface->launch同步启动;执行完毕后再用for循环执行winterface->sync等待所有worker完成,并且最后还用pbi->mb.corrupted和bit_reader_end记下了返回值。
很好理解。
// Accumulate thread frame counts.
if (!cm->frame_parallel_decoding_mode) {
for (n = 0; n < num_workers; ++n) {
TileWorkerData *const tile_data =
(TileWorkerData *)pbi->tile_workers[n].data1;
vp9_accumulate_frame_counts(&cm->counts, &tile_data->counts, 1);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
增长线程帧计数?
assert(bit_reader_end || pbi->mb.corrupted);
return bit_reader_end;
}
2
3
最后判断一下前面记下的返回值pbi->mb.corrupted和bit_reader_end是否正常,然后退出。
# decode_tiles
再来看单线程解码的decode_tiles
static const uint8_t *decode_tiles(VP9Decoder *pbi, const uint8_t *data,
const uint8_t *data_end) {
VP9_COMMON *const cm = &pbi->common;
const VPxWorkerInterface *const winterface = vpx_get_worker_interface();
const int aligned_cols = mi_cols_aligned_to_sb(cm->mi_cols);
const int tile_cols = 1 << cm->log2_tile_cols;
const int tile_rows = 1 << cm->log2_tile_rows;
2
3
4
5
6
7
初始化的方式和decode_tiles_mt里面差不多。但是这里多一个aligned_cols,从后面的代码看应该是和buffer大小有关的量。
TileBuffer tile_buffers[4][1 << 6];
int tile_row, tile_col;
int mi_row, mi_col;
TileWorkerData *tile_data = NULL;
2
3
4
TileBuffer直接在这初始化了,TileWorkerData也只有一个不像decode_tiles_mt里面每个线程都有一个TileWorkerData,果然是单线程,很合理。
if (cm->lf.filter_level && !cm->skip_loop_filter &&
pbi->lf_worker.data1 == NULL) {
CHECK_MEM_ERROR(cm, pbi->lf_worker.data1,
vpx_memalign(32, sizeof(LFWorkerData)));
pbi->lf_worker.hook = vp9_loop_filter_worker;
if (pbi->max_threads > 1 && !winterface->reset(&pbi->lf_worker)) {
vpx_internal_error(&cm->error, VPX_CODEC_ERROR,
"Loop filter thread creation failed");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
从《libvpx解码过程解读》里已经知道,多线程decode_tiles_mt的情况下环路滤波的过程是在外面调用的,decode_tiles_row_wise_mt和单线程的decode_tiles里面自带环路滤波。
这里就是给环路滤波分配数据,并且pbi->lf_worker.hook = vp9_loop_filter_worker给环路滤波的hook赋了值。
if (cm->lf.filter_level && !cm->skip_loop_filter) {
LFWorkerData *const lf_data = (LFWorkerData *)pbi->lf_worker.data1;
// Be sure to sync as we might be resuming after a failed frame decode.
winterface->sync(&pbi->lf_worker);
vp9_loop_filter_data_reset(lf_data, get_frame_new_buffer(cm), cm,
pbi->mb.plane);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
从注释上看应该是确保环路滤波的hook已经正确退出。
assert(tile_rows <= 4);
assert(tile_cols <= (1 << 6));
2
两个判断,这里怎么是assert(tile_rows <= 4),多线程decode_tiles_mt那里却是assert(tile_rows == 1)?怪
// Note: this memset assumes above_context[0], [1] and [2]
// are allocated as part of the same buffer.
memset(cm->above_context, 0,
sizeof(*cm->above_context) * MAX_MB_PLANE * 2 * aligned_cols);
memset(cm->above_seg_context, 0,
sizeof(*cm->above_seg_context) * aligned_cols);
vp9_reset_lfm(cm);
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
重置了一些内存空间。
这里的context应该是是指熵解码context,lfm应该是指用于环路滤波的内存空间。
get_tile_buffers(pbi, data, data_end, tile_cols, tile_rows, tile_buffers);
和decode_tiles_mt里一样,一个get_tile_buffers把data里的tile数据加载到buffer里。只不过前面的多线程是加载到pbi->tile_buffers里,这里直接是加载到函数开头定义的tile_buffers里
// Load all tile information into tile_data.
for (tile_row = 0; tile_row < tile_rows; ++tile_row) {
for (tile_col = 0; tile_col < tile_cols; ++tile_col) {
const TileBuffer *const buf = &tile_buffers[tile_row][tile_col];
tile_data = pbi->tile_worker_data + tile_cols * tile_row + tile_col;
tile_data->xd = pbi->mb;
tile_data->xd.corrupted = 0;
tile_data->xd.counts =
cm->frame_parallel_decoding_mode ? NULL : &cm->counts;
vp9_zero(tile_data->dqcoeff);
vp9_tile_init(&tile_data->xd.tile, cm, tile_row, tile_col);
setup_token_decoder(buf->data, data_end, buf->size, &cm->error,
&tile_data->bit_reader, pbi->decrypt_cb,
pbi->decrypt_state);
vp9_init_macroblockd(cm, &tile_data->xd, tile_data->dqcoeff);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
这个操作对应的是decode_tiles_mt里的排序之后分配任务的操作。从前面decode_tiles_mt里可以看到,分配任务本质上就是给每个线程专用的buffer里面放上数据。这里是单线程,所以也不需要什么排序,直接无脑拷贝就行了。
for (tile_row = 0; tile_row < tile_rows; ++tile_row) {
TileInfo tile;
vp9_tile_set_row(&tile, cm, tile_row);
for (mi_row = tile.mi_row_start; mi_row < tile.mi_row_end;
mi_row += MI_BLOCK_SIZE) {
for (tile_col = 0; tile_col < tile_cols; ++tile_col) {
const int col =
pbi->inv_tile_order ? tile_cols - tile_col - 1 : tile_col;
tile_data = pbi->tile_worker_data + tile_cols * tile_row + col;
vp9_tile_set_col(&tile, cm, col);
vp9_zero(tile_data->xd.left_context);
vp9_zero(tile_data->xd.left_seg_context);
for (mi_col = tile.mi_col_start; mi_col < tile.mi_col_end;
mi_col += MI_BLOCK_SIZE) {
if (pbi->row_mt == 1) {
int plane;
RowMTWorkerData *const row_mt_worker_data = pbi->row_mt_worker_data;
for (plane = 0; plane < MAX_MB_PLANE; ++plane) {
tile_data->xd.plane[plane].eob = row_mt_worker_data->eob[plane];
tile_data->xd.plane[plane].dqcoeff =
row_mt_worker_data->dqcoeff[plane];
}
tile_data->xd.partition = row_mt_worker_data->partition;
process_partition(tile_data, pbi, mi_row, mi_col, BLOCK_64X64, 4,
PARSE, parse_block);
for (plane = 0; plane < MAX_MB_PLANE; ++plane) {
tile_data->xd.plane[plane].eob = row_mt_worker_data->eob[plane];
tile_data->xd.plane[plane].dqcoeff =
row_mt_worker_data->dqcoeff[plane];
}
tile_data->xd.partition = row_mt_worker_data->partition;
process_partition(tile_data, pbi, mi_row, mi_col, BLOCK_64X64, 4,
RECON, recon_block);
} else {
decode_partition(tile_data, pbi, mi_row, mi_col, BLOCK_64X64, 4);
}
}
pbi->mb.corrupted |= tile_data->xd.corrupted;
if (pbi->mb.corrupted)
vpx_internal_error(&cm->error, VPX_CODEC_CORRUPT_FRAME,
"Failed to decode tile data");
}
// Loopfilter one row.
if (cm->lf.filter_level && !cm->skip_loop_filter) {
const int lf_start = mi_row - MI_BLOCK_SIZE;
LFWorkerData *const lf_data = (LFWorkerData *)pbi->lf_worker.data1;
// delay the loopfilter by 1 macroblock row.
if (lf_start < 0) continue;
// decoding has completed: finish up the loop filter in this thread.
if (mi_row + MI_BLOCK_SIZE >= cm->mi_rows) continue;
winterface->sync(&pbi->lf_worker);
lf_data->start = lf_start;
lf_data->stop = mi_row;
if (pbi->max_threads > 1) {
winterface->launch(&pbi->lf_worker);
} else {
winterface->execute(&pbi->lf_worker);
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
这就是主要的处理操作了。这一看就是几个for循环一行一行一列一列地在处理数据。到这里都没有decode_tiles_mt里看到的tile_worker_hook出场,说明tile_worker_hook肯定是被分解了放在这个循环里面了,所以这循环里面的操作应该和我们之后要研究的tile_worker_hook里的操作大差不离。
再仔细看看,除了一堆赋值的操作和最后明显是执行环路滤波的操作之外,就只有pbi->row_mt == 1时最后调用的process_partition还有else时调用的decode_partition了,这两个操作应该就是更底层的解码函数,tile_worker_hook里调用的应该也是这两个。并且从它们的执行条件看,process_partition是pbi->row_mt == 1时调用的,那decode_partition估计也就是通过多次调用process_partition实现的。
// Loopfilter remaining rows in the frame.
if (cm->lf.filter_level && !cm->skip_loop_filter) {
LFWorkerData *const lf_data = (LFWorkerData *)pbi->lf_worker.data1;
winterface->sync(&pbi->lf_worker);
lf_data->start = lf_data->stop;
lf_data->stop = cm->mi_rows;
winterface->execute(&pbi->lf_worker);
}
// Get last tile data.
tile_data = pbi->tile_worker_data + tile_cols * tile_rows - 1;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
看来是上面的循环里面不一定能完成全部的环路滤波?
return vpx_reader_find_end(&tile_data->bit_reader);
}
2
最后是读完终止数据后结束。
总结一下,多线程解码底层每个线程都是在调用tile_worker_hook,而从这个函数看,更底层的除了函数应该就是process_partition和decode_partition,tile_worker_hook应该也是调用的process_partition和decode_partition。
接下来继续看decode_partition:《libvpx中的decode_partition》。
