Nerf运行流程解析
上接:体渲染
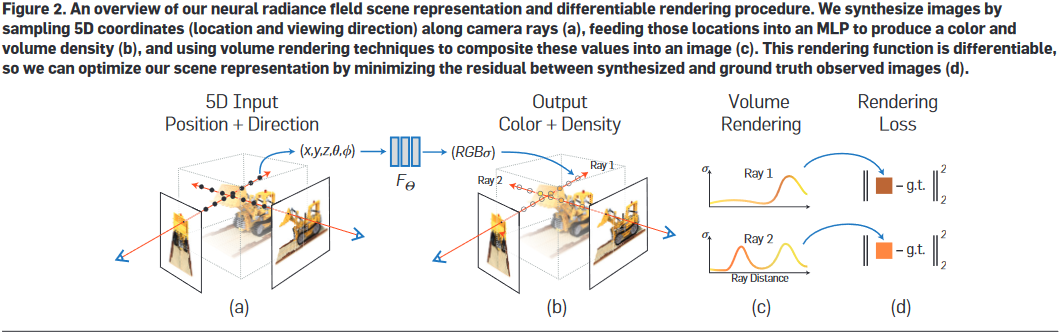
从论文中给出的系统结构图可知,Nerf中的DNN输入是相机位置(x,y,z)和射线朝向(θ,ϕ),其组成5元组表示一条光路;DNN输出是这条光路的各离散采样区间δn内的粒子颜色cn和其粒子密度σn(即光学厚度),之后,按照上述离散化体渲染公式进行积分操作,即得到这条光路射出的光线颜色,就像这样:
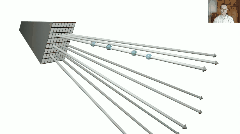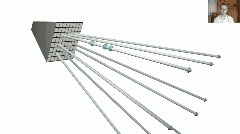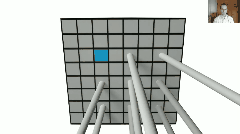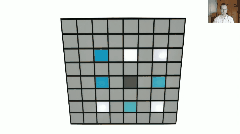
于是,渲染过程如下:
- 指定相机的外参(位置、方向等)和内参(焦距、视野、分辨率等)根据外参内参计算出需要采样的各光路的(x,y,z,θ,ϕ)
- 将每个光路的(x,y,z,θ,ϕ)输入DNN,计算得到光路上各离散采样区间δn内的颜色cn和粒子密度σn
- 按照离散化体渲染公式进行积分操作,即得到每条采样光路的颜色
- 根据这些采样光路的颜色和相机内参,计算出相机拍到的图像
- 上面这个离散化体渲染公式很显然是可微的,所以将计算得到的图像和Ground truth作差进行反向传播训练。
# 根据相机外参计算需要采样的光路
H, W是分辨率- 内参矩阵输入
K = np.array([[focal, 0, 0.5W], [0, focal, 0.5H], [0, 0, 1]])是焦距之类的 - 外参矩阵输入
c2w表示“Camera-to-world transformation matrix”,一个3x4矩阵 - 输出
rays_o, rays_d大小都是(H, W, 3)分别表示图像上各像素点对应需要采样的光线的原点和方向
# 函数render
def render(H, W, K, chunk=1024*32, rays=None, c2w=None, ndc=True,
near=0., far=1.,
use_viewdirs=False, c2w_staticcam=None,
**kwargs):
"""Render rays
Args:
H: int. Height of image in pixels.
W: int. Width of image in pixels.
focal: float. Focal length of pinhole camera.
chunk: int. Maximum number of rays to process simultaneously. Used to
control maximum memory usage. Does not affect final results.
rays: array of shape [2, batch_size, 3]. Ray origin and direction for
each example in batch.
c2w: array of shape [3, 4]. Camera-to-world transformation matrix.
ndc: bool. If True, represent ray origin, direction in NDC coordinates.
near: float or array of shape [batch_size]. Nearest distance for a ray.
far: float or array of shape [batch_size]. Farthest distance for a ray.
use_viewdirs: bool. If True, use viewing direction of a point in space in model.
c2w_staticcam: array of shape [3, 4]. If not None, use this transformation matrix for
camera while using other c2w argument for viewing directions.
Returns:
rgb_map: [batch_size, 3]. Predicted RGB values for rays.
disp_map: [batch_size]. Disparity map. Inverse of depth.
acc_map: [batch_size]. Accumulated opacity (alpha) along a ray.
extras: dict with everything returned by render_rays().
"""
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
if c2w is not None:
# special case to render full image
rays_o, rays_d = get_rays(H, W, K, c2w)
else:
# use provided ray batch
rays_o, rays_d = rays
if use_viewdirs:
# provide ray directions as input
viewdirs = rays_d
if c2w_staticcam is not None:
# special case to visualize effect of viewdirs
rays_o, rays_d = get_rays(H, W, K, c2w_staticcam)
viewdirs = viewdirs / torch.norm(viewdirs, dim=-1, keepdim=True)
viewdirs = torch.reshape(viewdirs, [-1,3]).float()
sh = rays_d.shape # [..., 3]
if ndc:
# for forward facing scenes
rays_o, rays_d = ndc_rays(H, W, K[0][0], 1., rays_o, rays_d)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
如果输入了rays就直接用,否则就用c2w或者c2w_staticcam算出rays_o和rays_d。
# Create ray batch
rays_o = torch.reshape(rays_o, [-1,3]).float()
rays_d = torch.reshape(rays_d, [-1,3]).float()
2
3
reshape成Batch。因为计算过程以光线为单位,不需要管光线对应图片上的哪个像素。
near, far = near * torch.ones_like(rays_d[...,:1]), far * torch.ones_like(rays_d[...,:1])
rays = torch.cat([rays_o, rays_d, near, far], -1)
if use_viewdirs:
rays = torch.cat([rays, viewdirs], -1)
2
3
4
这是把rays和光线的最近最远距离合并,作为模型的输入。
# Render and reshape
all_ret = batchify_rays(rays, chunk, **kwargs)
for k in all_ret:
k_sh = list(sh[:-1]) + list(all_ret[k].shape[1:])
all_ret[k] = torch.reshape(all_ret[k], k_sh)
k_extract = ['rgb_map', 'disp_map', 'acc_map']
ret_list = [all_ret[k] for k in k_extract]
ret_dict = {k : all_ret[k] for k in all_ret if k not in k_extract}
return ret_list + [ret_dict]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
这是执行推断过程,输出结果。结果为每个像素的颜色和视差。
# 函数batchify_rays
就是根据输入的batch size将输入的rays分批调用render_rays。
# 函数render_rays
def render_rays(ray_batch,
network_fn,
network_query_fn,
N_samples,
retraw=False,
lindisp=False,
perturb=0.,
N_importance=0,
network_fine=None,
white_bkgd=False,
raw_noise_std=0.,
verbose=False,
pytest=False):
"""Volumetric rendering.
Args:
ray_batch: array of shape [batch_size, ...]. All information necessary
for sampling along a ray, including: ray origin, ray direction, min
dist, max dist, and unit-magnitude viewing direction.
network_fn: function. Model for predicting RGB and density at each point
in space.
network_query_fn: function used for passing queries to network_fn.
N_samples: int. Number of different times to sample along each ray.
retraw: bool. If True, include model's raw, unprocessed predictions.
lindisp: bool. If True, sample linearly in inverse depth rather than in depth.
perturb: float, 0 or 1. If non-zero, each ray is sampled at stratified
random points in time.
N_importance: int. Number of additional times to sample along each ray.
These samples are only passed to network_fine.
network_fine: "fine" network with same spec as network_fn.
white_bkgd: bool. If True, assume a white background.
raw_noise_std: ...
verbose: bool. If True, print more debugging info.
Returns:
rgb_map: [num_rays, 3]. Estimated RGB color of a ray. Comes from fine model.
disp_map: [num_rays]. Disparity map. 1 / depth.
acc_map: [num_rays]. Accumulated opacity along each ray. Comes from fine model.
raw: [num_rays, num_samples, 4]. Raw predictions from model.
rgb0: See rgb_map. Output for coarse model.
disp0: See disp_map. Output for coarse model.
acc0: See acc_map. Output for coarse model.
z_std: [num_rays]. Standard deviation of distances along ray for each
sample.
"""
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
N_rays = ray_batch.shape[0]
rays_o, rays_d = ray_batch[:,0:3], ray_batch[:,3:6] # [N_rays, 3] each
viewdirs = ray_batch[:,-3:] if ray_batch.shape[-1] > 8 else None
bounds = torch.reshape(ray_batch[...,6:8], [-1,1,2])
near, far = bounds[...,0], bounds[...,1] # [-1,1]
t_vals = torch.linspace(0., 1., steps=N_samples)
if not lindisp:
z_vals = near * (1.-t_vals) + far * (t_vals)
else:
z_vals = 1./(1./near * (1.-t_vals) + 1./far * (t_vals))
z_vals = z_vals.expand([N_rays, N_samples])
if perturb > 0.:
# get intervals between samples
mids = .5 * (z_vals[...,1:] + z_vals[...,:-1])
upper = torch.cat([mids, z_vals[...,-1:]], -1)
lower = torch.cat([z_vals[...,:1], mids], -1)
# stratified samples in those intervals
t_rand = torch.rand(z_vals.shape)
# Pytest, overwrite u with numpy's fixed random numbers
if pytest:
np.random.seed(0)
t_rand = np.random.rand(*list(z_vals.shape))
t_rand = torch.Tensor(t_rand)
z_vals = lower + (upper - lower) * t_rand
pts = rays_o[...,None,:] + rays_d[...,None,:] * z_vals[...,:,None] # [N_rays, N_samples, 3]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
这是在输入的光路上生成N_samples个采样点。
# raw = run_network(pts)
raw = network_query_fn(pts, viewdirs, network_fn)
rgb_map, disp_map, acc_map, weights, depth_map = raw2outputs(raw, z_vals, rays_d, raw_noise_std, white_bkgd, pytest=pytest)
2
3
这是调用DNN推断输出计算结果。network_query_fn是外面输入的模型推断函数,输入是每条光线上的每个采样点位置,输出是每条光线的各离散采样区间δn内的颜色cn和粒子密度σn;raw2outputs是将模型输出进行积分得到每条光线的颜色。
if N_importance > 0:
rgb_map_0, disp_map_0, acc_map_0 = rgb_map, disp_map, acc_map
z_vals_mid = .5 * (z_vals[...,1:] + z_vals[...,:-1])
z_samples = sample_pdf(z_vals_mid, weights[...,1:-1], N_importance, det=(perturb==0.), pytest=pytest)
z_samples = z_samples.detach()
z_vals, _ = torch.sort(torch.cat([z_vals, z_samples], -1), -1)
pts = rays_o[...,None,:] + rays_d[...,None,:] * z_vals[...,:,None] # [N_rays, N_samples + N_importance, 3]
run_fn = network_fn if network_fine is None else network_fine
# raw = run_network(pts, fn=run_fn)
raw = network_query_fn(pts, viewdirs, run_fn)
rgb_map, disp_map, acc_map, weights, depth_map = raw2outputs(raw, z_vals, rays_d, raw_noise_std, white_bkgd, pytest=pytest)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
这多算几次?
ret = {'rgb_map' : rgb_map, 'disp_map' : disp_map, 'acc_map' : acc_map}
if retraw:
ret['raw'] = raw
if N_importance > 0:
ret['rgb0'] = rgb_map_0
ret['disp0'] = disp_map_0
ret['acc0'] = acc_map_0
ret['z_std'] = torch.std(z_samples, dim=-1, unbiased=False) # [N_rays]
for k in ret:
if (torch.isnan(ret[k]).any() or torch.isinf(ret[k]).any()) and DEBUG:
print(f"! [Numerical Error] {k} contains nan or inf.")
return ret
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# 函数raw2outputs
def raw2outputs(raw, z_vals, rays_d, raw_noise_std=0, white_bkgd=False, pytest=False):
"""Transforms model's predictions to semantically meaningful values.
Args:
raw: [num_rays, num_samples along ray, 4]. Prediction from model.
z_vals: [num_rays, num_samples along ray]. Integration time.
rays_d: [num_rays, 3]. Direction of each ray.
Returns:
rgb_map: [num_rays, 3]. Estimated RGB color of a ray.
disp_map: [num_rays]. Disparity map. Inverse of depth map.
acc_map: [num_rays]. Sum of weights along each ray.
weights: [num_rays, num_samples]. Weights assigned to each sampled color.
depth_map: [num_rays]. Estimated distance to object.
"""
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
输入的raw是每条光线上各离散采样区间内颜色和概率密度,即DNN的输出、z_vals是每条光线上每个采样区间的长度、rays_d是每条光线的方向。
主要输出rgb_map是每条光线的颜色、disp_map是每条光线的视差、depth_map是每条光线的深度。
raw2alpha = lambda raw, dists, act_fn=F.relu: 1.-torch.exp(-act_fn(raw)*dists)
raw2alpha对应体渲染公式中的1−e−σnδn。
dists = z_vals[...,1:] - z_vals[...,:-1]
dists = torch.cat([dists, torch.Tensor([1e10]).expand(dists[...,:1].shape)], -1) # [N_rays, N_samples]
2
每条光线的离散采样区间从0开始计算距离。
dists = dists * torch.norm(rays_d[...,None,:], dim=-1)
这个应该是归一化之类的操作。
rgb = torch.sigmoid(raw[...,:3]) # [N_rays, N_samples, 3]
看来raw[...,:3]里面就是每个采样点的颜色数据。
noise = 0.
if raw_noise_std > 0.:
noise = torch.randn(raw[...,3].shape) * raw_noise_std
# Overwrite randomly sampled data if pytest
if pytest:
np.random.seed(0)
noise = np.random.rand(*list(raw[...,3].shape)) * raw_noise_std
noise = torch.Tensor(noise)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
测试时可以加噪声。
alpha = raw2alpha(raw[...,3] + noise, dists) # [N_rays, N_samples]
算1−e−σnδn。
# weights = alpha * tf.math.cumprod(1.-alpha + 1e-10, -1, exclusive=True)
weights = alpha * torch.cumprod(torch.cat([torch.ones((alpha.shape[0], 1)), 1.-alpha + 1e-10], -1), -1)[:, :-1]
2
这里torch.cumprod是在算Tn=e−∑k=1n−1σkδk,weights对应的是Tn(1−e−σnδn)。
rgb_map = torch.sum(weights[...,None] * rgb, -2) # [N_rays, 3]
积分求颜色,一看就懂。
depth_map = torch.sum(weights * z_vals, -1)
disp_map = 1./torch.max(1e-10 * torch.ones_like(depth_map), depth_map / torch.sum(weights, -1))
acc_map = torch.sum(weights, -1)
if white_bkgd:
rgb_map = rgb_map + (1.-acc_map[...,None])
return rgb_map, disp_map, acc_map, weights, depth_map
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
计算每条光线的深度depth_map和视差disp_map,还把weights求了个和作为acc_map。
在最后的输出中,这里几个东西都没用上,训练过程只用了颜色rgb与Groung-truth求差。
